It is a well known fact that horticultural knowledge and skills should be on par with the creative side of Bonsai cultivation as a horticulturally neglected tree will never reach its full potential as a Bonsai. It is therefore important that some basic horticultural knowledge and skills are mastered early on the journey towards Bonsai mastery.
This series of articles has it as goal to highlight a few processes in horticultural science and linking this knowledge to Bonsai creation and maintenance. We will start off with the most important one and that is Photosynthesis. Others will follow in subsequent articles.

Photosynthesis
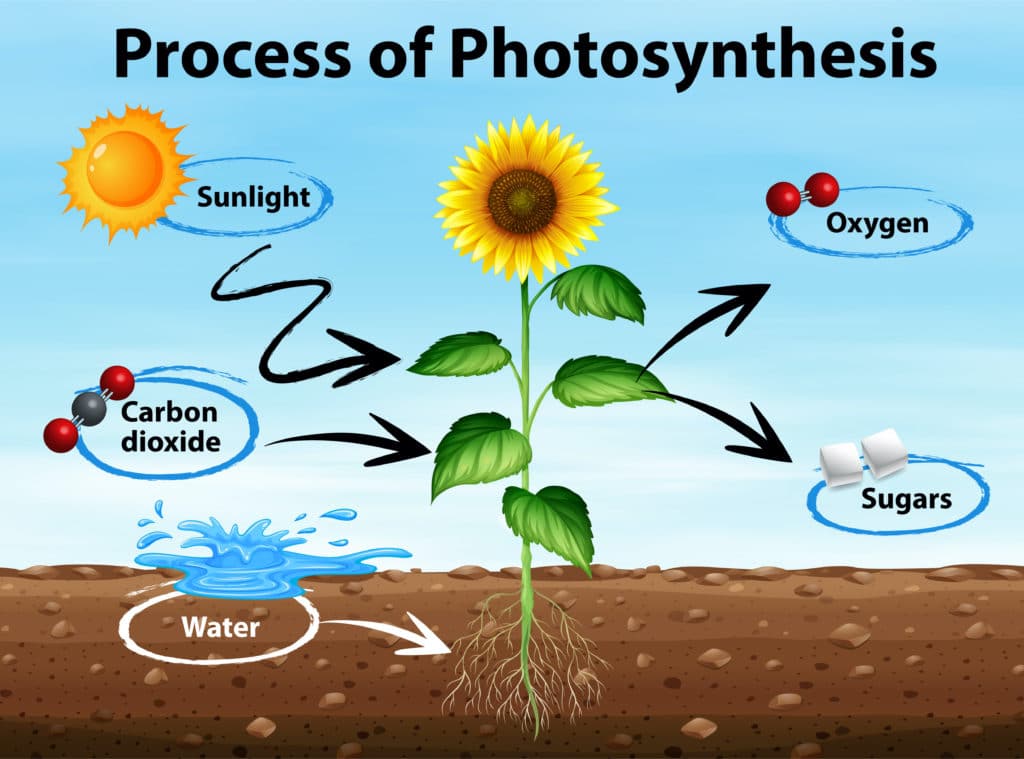
A bit of knowledge relating to cell science will help here. In plant cells, usually where there is a green colour, you will find cell organelles called chloroplasts. Inside these there is chlorophyll, a colour pigment, and this one is attributed to the green colour in plants. This is where photosynthesis takes place. Photosynthesis is the process through which plants use raw material to produce food. The raw materials are carbon dioxide and water and with the aid of energy from the sun, food is produced and oxygen is made as a by-product of this process.
What does this mean for Bonsai? The most important part here is the exposure to light. Without this natural light source not enough energy will be available for this process. The second part is that there should be enough chloroplasts available for this process to take place. The significance of this comes in at pruning time. It needs to be at the right time as there should be enough energy / food stored to carry the tree through the period with either no leaves or very few leaves, as at this time food production will be limited. This is crucial for evergreens as the food storage or energy storage side of these plants are not as well developed as what it is for deciduous plants. See the process of transpiration in another article as it plays a role with this as well.
In summary:
- Your tree should have adequate light for food production.
- Your tree should have adequate water for food production. Water plays a role in other processes as well which makes watering a crucial task for healthy Bonsai growing. See transpiration as an example.
- Adequate ventilation is necessary to allow atmospheric carbon dioxide to get to your tree. This is usually not a problem in the outdoors, but something to think about when you cover trees with plastic to increase heat and humidity for growth purposes or other climatic defensive reasons.
- Pruning and defoliating. Time this right. Never defoliate an evergreen completely unless it is just a branch or two for the purpose of creating deadwood / Jin.
- When positioning branches and foliage pads, make sure that top branches do not cover lower branches too much.
Please like or comment on this post and subscribe for regular updates. It will cost you nothing.
Subscribing will help as you will get the updates for the other processes covered in this series. That includes transpiration, respiration, growth, secondary thickening, tropisms and the importance of hormones in all of this.